Environmental Settings
Using Environmental Settings within APCC can improve your pointing and tracking accuracy when doing things like sky modeling and refraction calculations.
APCC's Environmental polling uses the ASCOM standard ObservingConditions hub, so it can work with THUM devices, OpenWeatherMap, or any device or service that provides an ASCOM ObservingConditions driver. This includes:
•Pegasus Astro Uranus Meteo
•Pegasus Astro PowerBox (with environmental sensor)
•MGBox V2
If you are interesting in experimenting with Environmental Settings but don't want to invest in a dedicated monitor, you can try OpenWeatherMap which is a no cost source of weather data. Details on how to do this are in the following knowledgebase article: https://astro-physics.bolddesk.com/kb/article/61/how-to-set-your-location-for-environmental-variables-in-openweathermap
Open the Environmental Settings to configure the
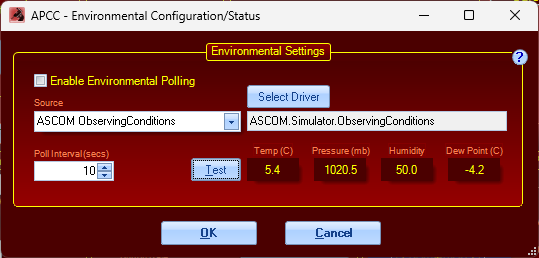
Enable Environmental Polling - turns on/off environmental polling
Source - you can choose THUM Device or ASCOM ObservingConditions. The source will need to be properly installed and configured prior to connecting in APCC.
Poll interval (secs) - how often is the device polled for updated conditions. Generally the default value of 10 seconds is sufficient for most situations.
Select Driver - If you chose ASCOM ObservingConditions, you need to select the specific device/driver.
Test - once your device is properly configured, you can click Test button to test the connection. If it works properly, you will see values for one or more of the environmental variables (please note your device may not support all variables. For example, pressure is often omitted from some results). Also note with MGBox V2 if it returns -273c for temperature, that indicates the device is not yet initialized, or it is not working properly. Consult the product documentation for possible fixes.
Once your Environmental Settings are correctly configured, you can enable environmental polling in APPM's general information tab to further refine your sky modeling results.
